Traditionally, growth for B2B products came from hefty investments in sales and marketing. Companies like SAP and Oracle relied on substantial sales teams and marketing campaigns to secure large enterprise contracts. Then, companies like Dropbox and Slack approached go-to-market with a new motion called Product-Led Growth (PLG). The idea is straightforward: create a product that users love, encourage easy adoption, and then use those enthusiastic users to win over the entire company.
But there's a catch. While PLG can drive rapid initial success, driving a sustainable Product-Led Growth strategy presents considerable challenges.
This is where Product Growth Managers come in. The Growth Manager is a type of Product Manager who plays a crucial role in navigating the challenges of keeping things moving ‘up and to the right.’ They ensure that the product not only attracts users but also grows efficiently as the company scales. In this article, we'll explore how Product Growth Managers are essential in guiding companies through the complexities of the PLG journey.
I actually think every PM needs to be a Growth PM. Below, I’ll discuss my experience and what it has taught me about the need for sustainable growth strategies. I’ll also talk about the skills, experience, and knowledge it takes to become a Growth Product Manager today.
Product Experimentation Certification
Scale growth through data-driven testing. Use AI to optimize acquisition, retention, pricing, and build a culture of high-velocity experiments.
Enroll now
What Is a Growth Product Manager?
A Growth Product Manager (GPM) is a role focused on driving expansion and scaling a product. A Growth Product Manager’s job description focuses on metrics that indicate growth, such as user acquisition, retention, engagement, and monetization. Growth managers often, but not always, work on cross-functional growth teams who experiment with different levers for growth.
Why are Growth Product Managers in such high demand?
The majority of us product folks have spent our careers building and learning in a bull market. Between 2010 and 2022, the market largely moved up and to the right, driven by digital transformation in the workplace, the rise of app stores and open marketplaces, and the growing dominance of apps and services that captivated consumer attention. Growth at all costs became the expectation, and it was rewarded—thanks to the low cost of capital. Until it wasn’t - the market shifted, and sustainable, long-term growth with durable business models became the new expectation. The old playbook of throwing money at a product to drive growth went defunct.
I was leading product teams at Meta when this market shift happened, and I quickly learned what a Product Manager (PM) needed to succeed in this new environment. Product Managers who could drive effective and efficient distribution were poised to rise to the top. Mastering the art and science of growth, experimentation, and precise product optimizations was what businesses now needed. PMs and their teams were expected to be ROI-positive, which reshaped my understanding of the PM role.
PMs were no longer simply tasked with delivering features; we were now accountable for driving revenue and product success through growth metrics that directly impacted the profit and loss (P&L). This shift reflects a broader trend that has been gaining slow momentum over the past decade or so and is now more critical than ever. Growth is not new — Meta pioneered dedicated growth teams back in 2007— but it’s now becoming a standard expectation across the industry.
Reflecting on this changing market landscape and the skills that the next generation of product leaders will need to succeed, three critical areas come to my mind: accountability for revenue, an understanding of Product-Led Growth (PLG), and retention as a key driver of growth. Mastering these aren’t just advantageous; they are essential for PMs who want to create meaningful impact for their customers and win in today’s competitive landscape.
Growth Product Manager vs. Product Manager
People often ask what the difference is between a Growth PM and a regular PM. The question presumes that one is either a Product Manager or a Growth Product Manager. In reality, it’s not either/or; it’s both/and. Growth Product Managers do what any other Product Manager does, but they do it with growth as their goal. This focus informs their day-to-day tasks, the skills they hone, and their responsibilities within their organizations.
3 reasons why every Product Manager needs to be a Growth Product Manager
1. PMs Are Now Accountable for Revenue
Product Managers must take ownership of growth metrics to drive significant business impact. This requires fluency in metrics like:
Activation: Essential for early engagement and sets the stage for retention.
Retention: Drives long-term user satisfaction and loyalty.
Lifetime Value (LTV): Indicates customer profitability and shapes acquisition strategies.
These metrics allow PMs to make data-driven decisions that align closely with business objectives, impacting both the top and bottom lines of the P&L. Setting specific, measurable goals—like a 10% increase in trial-to-paid conversions over the next quarter—is crucial. Continuous monitoring and adjustment based on performance can lead to substantial revenue growth, showing how even small improvements across the funnel compound into significant financial gains.
Growth strategies often yield a positive return on investment (ROI), with financial outcomes that more than justify the investment. PMs who understand how their decisions impact revenue can prioritize features that not only enhance user experience but also drive financial results for the business. However, as PMs become accountable for revenue, they must also understand how to use product levers to achieve scale — through PLG.
2. The Shift to Product-Led Growth (PLG)
The shift to Product-Led Growth (PLG) has redefined customer acquisition and retention strategies, emphasizing the product itself as the primary driver of growth. PLG minimizes friction in the user experience, leading to faster adoption and higher retention rates. Key elements of PLG include:
Freemium Models: Allow users to experience value before committing financially.
Self-Serve Funnels: Enable users to get started and realize product value without relying on sales teams.
Seamless Onboarding: Helps users immediately find value in a product, with every additional interaction offering increased value.
Companies prioritizing PLG can achieve rapid user adoption, as seen with Threads, which reached 100 million monthly active users (MAUs) just four days after launch. However, without retention strategies, high churn can quickly undermine initial success. A high user volume alone does not equate to sustainable growth.

In order to become a standout example of PLG, PMs must become growth-focused leaders who prioritize strategies that drive user acquisition and retention through the product itself. This requires a deep understanding of user behavior and a commitment to optimizing the product experience for maximum engagement and value. Embracing this growth mindset is no longer optional; it’s essential for PMs who want to succeed in a competitive landscape where product experience directly correlates with long-term business success—and this mindset is rooted in retention.
3. Retention Is the Key Driver of Growth
Retention isn’t just crucial—it’s the engine of sustainable growth. While acquiring new users is costly and resource-intensive, retaining them drives long-term value. Increasing retention by just 5% can boost profits by 25-95%, as loyal users contribute more via repeat purchases, higher LTV, and advocacy. Some strategies to drive retention include:
Personalized Experiences: Tailor the user experience to individual preferences, ensuring users quickly realize the product’s unique value.
Create Habitual Usage and Self-Sustaining Growth Loops: Design experiences that foster ongoing engagement, turning satisfied users into repeat users who drive organic retention and sustained product growth.
Understanding What Drives Retention: Identify which product features or values are clearly correlated—or even causal—to long-term retention, and ensure these are front and center in the user experience.
By internalizing the idea that “it’s all about retention,” Growth PMs can reduce acquisition costs while establishing a robust growth engine that scales efficiently. Spotify is an excellent example of this approach: personalized onboarding with music recommendations helps users quickly find value, while features like the annual “Wrapped” campaign foster ongoing engagement by highlighting users’ listening habits and encouraging them to share. Regular initiatives like “New Music Fridays” keep users returning for fresh content.
In a landscape where retention drives sustainable growth, PMs must focus on it to enhance user satisfaction and lay the groundwork for long-term business success.

What Does a Growth Product Manager Do?
Product-led growth is really just a recognition and a decision to say the product experience is a key driver of how we both acquire and expand usage.
— Berit Hoffmann, CPO at Sisu Data, in The Product Podcast
A GPM focuses on driving growth metrics like user acquisition, retention, and engagement. Their job revolves around identifying opportunities to expand the user base and optimize the product's performance. GPMs use data-driven approaches to analyze user behavior, run experiments, and refine the user journey to encourage growth. A GPM’s focus lies not on specific product offerings but on holistic growth and how the product experience can influence that growth, which is why they keep a close eye on product analytics and market performance.
For instance, a GPM might start their day by analyzing key metrics such as sign-ups and churn rates. They could then set up A/B tests to optimize onboarding flows and brainstorm new growth strategies like referral programs with the marketing team. The GPM’s day often ends with reviewing the results of experiments and planning future initiatives to grow the user base and enhance monetization.
Growth Product Manager Responsibilities
Data-Driven Decision Making: Growth Product Managers use product analytics to understand user behaviors and identify growth opportunities. They rely heavily on metrics like conversion rates, customer lifetime value (CLV), and churn rates to make informed decisions.
Experimentation and A/B Testing: A significant part of a GPM’s role involves running experiments to validate hypotheses about what drives growth. This could involve A/B testing different features, onboarding flows, or pricing strategies to see what resonates best with users.
Identify opportunities for growth: Whether through user-generated content or through referrals, GPMs are responsible for finding and exploiting growth loops that maximize growth within the product itself.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: GPMs work closely with marketing, engineering, design, and data science teams to implement growth strategies. They act as a bridge between these departments, ensuring that growth objectives are understood and pursued across the organization.
Optimization of the User Journey: They focus on optimizing the entire product experience, from the first interaction to becoming a loyal customer. This includes refining onboarding processes, reducing friction points, and enhancing user engagement, retention, and advocacy.
Strategic Planning: GPMs are responsible for setting growth goals and developing strategies to achieve them. They align their work with the broader business objectives and often play a key role in strategic decision-making processes.
Growth Product Manager Skills

Product Management: Leverage Product Manager skills to oversee the product's growth strategy, aligning features, user experience, and market needs to drive revenue and optimize engagement throughout the product lifecycle.
Analytics: Analyze user data to identify growth opportunities, track performance, and make data-driven decisions that enhance acquisition, retention, and revenue.
Marketing: Leverages marketing strategies to drive user acquisition and activation, integrating product growth goals with brand messaging, user engagement, and campaign optimization.
Data Science: Applies predictive models and machine learning to uncover insights, refine targeting, and personalize user experiences, enhancing growth through data-driven experimentation.
Design: Collaborates on user-centered designs to improve user journeys, optimize conversion, and ensure cohesive brand experiences that support product growth and user retention.
Customer Success: Aligns growth initiatives with customer support to ensure satisfaction, reduce churn, and identify customer feedback that informs product improvements and growth strategies.
How to Become a Growth Product Manager
Product Growth Certification (PGC)™
Ready to start today?
I partnered with Product School to create the Product Growth Certification (PGC)™, designed to equip you with the skills and strategies needed to drive product-led growth and increase revenue. This hands-on program teaches you how to leverage growth metrics, optimize user retention, and build scalable growth loops, empowering you to lead successful, growth-driven products. Take the next step in your career and start building products that deliver meaningful impact.
Product Experimentation Certification
Scale growth through data-driven testing. Use AI to optimize acquisition, retention, pricing, and build a culture of high-velocity experiments.
Enroll now
Hone Your Key Skills
To succeed as a Growth Product Manager, it's essential to develop specific skills:
Get Comfortable with Data: Dive into tools like SQL, Excel, and Google Analytics. Understanding data analytics is crucial for making informed decisions.
Learn Product Management Fundamentals: Familiarize yourself with the basics of product management, including user experience design, Agile methodologies, and understanding the product lifecycle.
Explore Growth Hacking Techniques: Master growth strategies, such as A/B testing, conversion rate optimization, and user acquisition methods.
Dive into Online Courses and Resources
Even if you aren’t ready to get certified yet, you can still take advantage of online courses that will start you on the right path. For a deep dive into Product-Led Strategies, check out Product School's Product-Led Growth micro-certification. Experience the game-changing potential of Product-Led Growth (PLG) as it revolutionizes the role of Product Managers and their impact on organizations. You can also check out helpful micro-certifications in product analytics and product strategy.
To dive deeper into Growth Strategies every PM should know, check out my webinar for Product School “Unlock Product Growth: Strategies Every PM Should Know:”
Gain Hands-On Experience
Apply what you've learned in real-world settings — serious companies will appreciate it. Look for roles like product analyst or marketing analyst, where you can get your hands on data and products more easily from the start. If it feels too quick too soon, internships and volunteer projects are also great ways to gain practical experience and build your portfolio.
Whatever your goal is, start building your resume and start now!
Network and Find Mentorship
Connect with other professionals in the field. Join communities on Slack, LinkedIn, attend local Meetup groups, or participate in online forums or subreddits. These networks can provide invaluable insights and opportunities. Finding a mentor can also be a game-changer. Connect with your senior peers who can offer guidance and advice tailored to your career path.
Discover the World's Largest Product Management Community
Join Product School's private Slack community and network with over 100,000 PMs.
Join Now
Stay Current and Keep Learning
The field of product management and growth is dynamic. As technology evolves — and it’s evolving rapidly — so does the Growth PM job requirement. Keep up with the latest trends by reading industry blogs, listening to relevant podcasts, and attending webinars. Product Management books can also offer deeper insights into growth strategies.
Most of the product management you learn is by doing. The theory is very limited. And that’s why I think it’s very important to be part of the community, to listen and learn from others, listen to podcasts, and read books.
— Rapha Cohen, CPO at Google's Waze, in The Product Podcast
Take the Leap into a Growth Product Manager Role
Once you have a solid foundation and some experience, start applying for Growth Product Manager roles. Tailor your resume to highlight your growth-related achievements, data-driven decisions, and any projects that demonstrate your ability to drive user engagement and retention. Showcase your passion for growth and your knack for experimentation.
Remember, every step you take brings you closer to becoming a successful Growth Product Manager. Keep learning, stay adaptable, and enjoy the journey!
Growth Product Manager Job Descriptions from Real Companies
Speaking of Growth PM roles, in this section, you'll find detailed job descriptions for Growth Product Manager positions at three well-known companies: ClassDojo, Time Doctor, and Triple Whale. Each description outlines the specific responsibilities, qualifications, and attributes these companies seek in their ideal candidates. By exploring these examples, you can gain an understanding of what it takes to succeed in this dynamic position.
Growth Product Manager Job Description #1 - ClassDojo
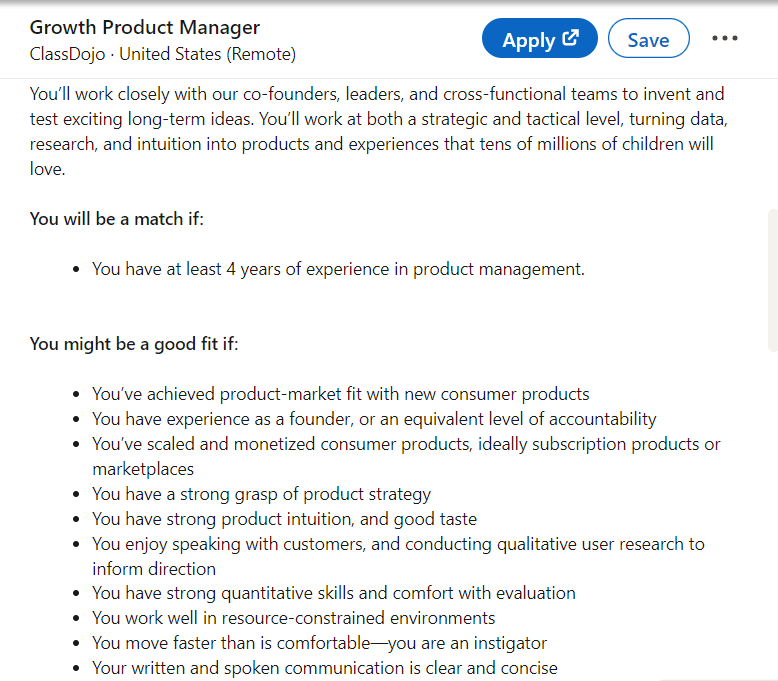
At ClassDojo, their ideal Growth Product Manager will collaborate closely with co-founders, leaders, and cross-functional teams to develop and test innovative, long-term concepts. The role requires working at both strategic and tactical levels, leveraging data, research, and intuition to create products and experiences that resonate with millions of children.
As is common around the industry, they want their candidates to have at least four years of experience in product management, having successfully achieved product-market fit with new consumer products.
Growth Product Manager Job Description #2 - Time Doctor
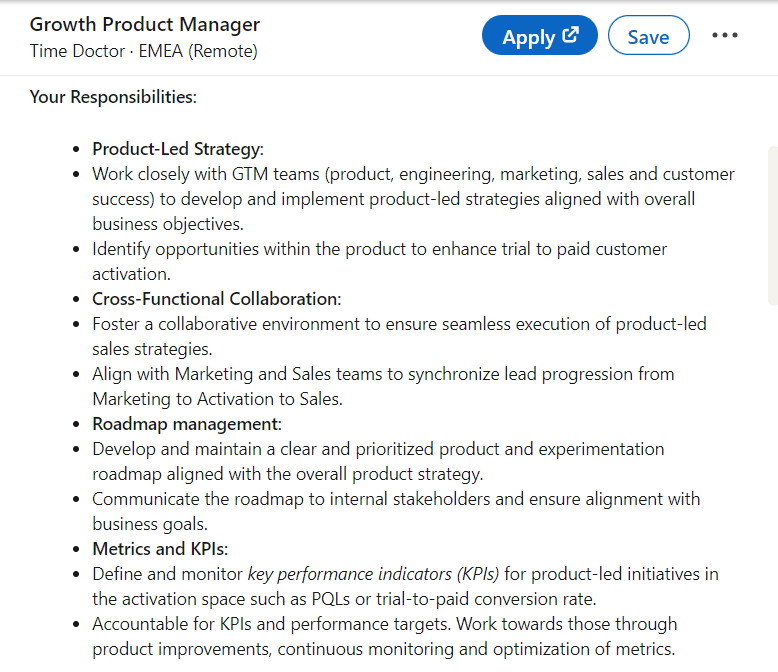
Time Doctor is looking for a Growth Product Manager who will work closely with GTM teams, including product, engineering, marketing, sales, and customer success, to develop and implement Product-Led Strategies.
The role involves identifying opportunities to enhance customer activation, fostering a collaborative environment for Product-Led Sales strategies, and managing product roadmap. The future employee will be responsible for defining and monitoring KPIs and aligning efforts with internal stakeholders to achieve business goals.
Again, strong skills in communication and collaboration, as well as a keen eye for data-driven decision-making, are cornerstones.
Triple Whale Growth Product Manager Job Description
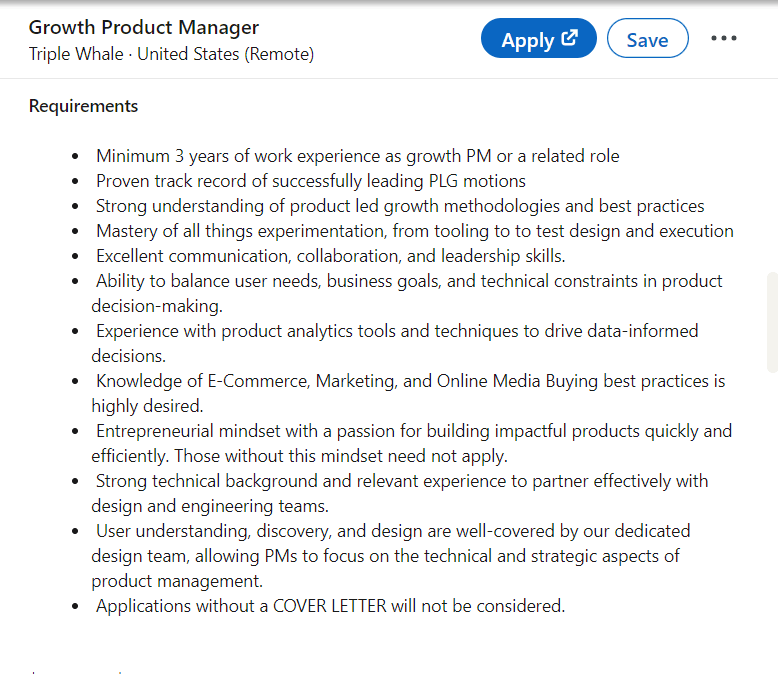
Triple Whale seeks a Growth Product Manager with a minimum of three years of experience in a Growth PM or related role. They want PM experienced in leading Product-Led Growth (PLG) initiatives.
Their ideal candidate has a strong understanding of PLG methodologies, expertise in experimentation, and proficiency with product analytics tools. They balance user needs, business goals, and technical constraints in their decision-making.
Here’s something specific to Triple Whale — a background in e-commerce, marketing, and online media buying is highly valued, alongside an entrepreneurial mindset and a passion for building impactful products efficiently.
Strong technical experience and the ability to partner effectively with design and engineering teams are also essential.
Action is Essential To Succeed as a GPM!
To all aspiring Growth Product Managers: now is the time to take action!
Start planning your career by building on your skills, aligning with your values, and following your dreams. Focus on learning, gaining experience, and connecting with others in the field. Remember, each step you take will serve your career path later on. Embrace the journey, stay curious, and keep pushing forward.
After all, it’s what growth is all about.
Product-Led Growth Micro-Certification (PLGC)™️
Experience the game-changing potential of Product-Led Growth (PLG) as it revolutionizes the role of Product Managers and their impact on organizations.
Enroll now for free
Updated: June 19, 2025